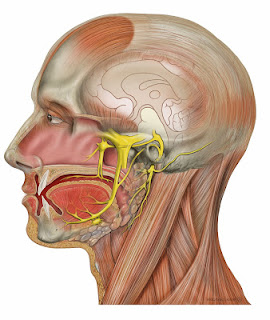
The Fifth or Trifacial Nerve (n. trigeminus) is the largest cranial nerve. It resembles a spinal nerve
(1) in arising by two roots; (2) in having a ganglion developed on its posterior root; and (3) in its function, since it is a compound nerve. It is the great sensory nerve of the head and face and the motor nerve of the muscles of mastication. Its upper two divisions are entirely sensory; the third division is partly sen.sory and partly motor. It arises by two roots: of these the anterior is the smaller, and is the motor root; the posterior, the larger and sensory. Its superficial origin is from the side of the pons Varolii, nearer to the upper than the lower border. The smaller root consists of three or four bundles; the larger root consists of numerous bundles of fibres, varying in number from,seventy to a hundred. The two roots are separated from one another by a few of the transverse fibres of the pons. 'I'he deep origin of the larger or sensory root is chiefly from a long tract in the medulla, the lower sensory nucleus. which is continuous below with the substantia gelatillosa of Rolando. '1'he fibres from t is nucleus form the so-called ascending root of the fifth; they pass upward -hrough the pons and join with fibres from the locus creruleus or upper sensory nucleus; which is situated to the outer side of the nucleus, from which the 10 er par of the motor root takes origin. The deep origin of the smaller or mot r root is derived partly from a nucleus embedded in the gray matter of the upper par- of the floor of the fourth ventricle and partly from a collection of ner.e-celh si uatad at the side of the aqueduct of Sylvius, from which the fibres pas;; Of) n ard under the name of the descending 1'00t of the fifth. The real origin 0; the sensory root is from the Gasserian ganglion, which corresponds with the ganglion on a spinal nerve (see Development of Spinal Nerves in section on EmhryolQ",The two roots of the nerve pass forward below the ten orium cerehelli as it bridges over the' notch on the inner part of the superior bor er of the petrous portion of the temporal bone: they then run between the bone and the dura. mater to the apex of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. where the fibres of the sensory root form a large semilunar ganglion (Gasserian). while the motor
(1) in arising by two roots; (2) in having a ganglion developed on its posterior root; and (3) in its function, since it is a compound nerve. It is the great sensory nerve of the head and face and the motor nerve of the muscles of mastication. Its upper two divisions are entirely sensory; the third division is partly sen.sory and partly motor. It arises by two roots: of these the anterior is the smaller, and is the motor root; the posterior, the larger and sensory. Its superficial origin is from the side of the pons Varolii, nearer to the upper than the lower border. The smaller root consists of three or four bundles; the larger root consists of numerous bundles of fibres, varying in number from,seventy to a hundred. The two roots are separated from one another by a few of the transverse fibres of the pons. 'I'he deep origin of the larger or sensory root is chiefly from a long tract in the medulla, the lower sensory nucleus. which is continuous below with the substantia gelatillosa of Rolando. '1'he fibres from t is nucleus form the so-called ascending root of the fifth; they pass upward -hrough the pons and join with fibres from the locus creruleus or upper sensory nucleus; which is situated to the outer side of the nucleus, from which the 10 er par of the motor root takes origin. The deep origin of the smaller or mot r root is derived partly from a nucleus embedded in the gray matter of the upper par- of the floor of the fourth ventricle and partly from a collection of ner.e-celh si uatad at the side of the aqueduct of Sylvius, from which the fibres pas;; Of) n ard under the name of the descending 1'00t of the fifth. The real origin 0; the sensory root is from the Gasserian ganglion, which corresponds with the ganglion on a spinal nerve (see Development of Spinal Nerves in section on EmhryolQ",The two roots of the nerve pass forward below the ten orium cerehelli as it bridges over the' notch on the inner part of the superior bor er of the petrous portion of the temporal bone: they then run between the bone and the dura. mater to the apex of the petrous portion of the temporal bone. where the fibres of the sensory root form a large semilunar ganglion (Gasserian). while the motor
Coin Casino | Casino Owned by Digimedia - CasinoWow
ReplyDeleteCoin Casino is a UK Online Casino. Our mission is 인카지노 to create the best online casino experience through the use 메리트 카지노 고객센터 of our febcasino platform and our